**What is a Communication Protocol?**
A communication protocol is a set of rules and conventions that define how data is transmitted between devices. In order for different data communication systems—often located in various geographical areas—to work together, they must have a common language. This ensures that information can be exchanged and resources shared effectively. The rules cover what to communicate, how to communicate, and when to communicate, forming the foundation of any successful data exchange.
**Three Elements of a Communication Protocol**
- **Syntax (Grammar):** Defines the structure of the data, including formatting, encoding, and signal levels.
- **Semantics:** Refers to the meaning of the data being transmitted, such as control signals, data content, and instructions.
- **Timing (Synchronization):** Specifies the sequence of events, rate matching, and ordering of data transmission.
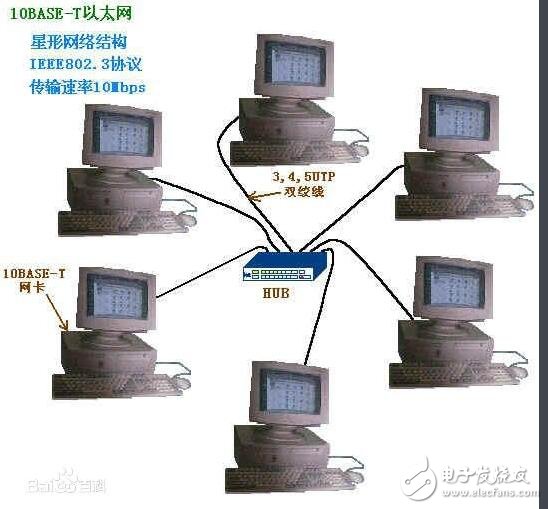
**Common Communication Protocols**
1. **TCP/IP**
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) originated from the ARPAnet project in the 1970s. It was developed by the U.S. Department of Defense to enable communication across different networks. This protocol suite includes TCP, IP, UDP, ARP, and ICMP, among others. Due to its scalability, security, and cross-platform compatibility, it has become the standard for internet communication. It is widely used in both local and wide area networks, and most modern operating systems come with it pre-installed.
2. **NetBEUI**
NetBEUI (NetBIOS Enhanced User Interface) is a fast and efficient protocol designed for small Windows-based LANs. It requires minimal configuration and consumes fewer network resources. However, it lacks routing capabilities and supports only up to 254 nodes, making it unsuitable for larger networks.
3. **IPX/SPX**
IPX/SPX (Internetwork Packet Exchange/Sequenced Packet Exchange) was primarily used in Novell NetWare networks. It allowed communication between different operating systems, such as Windows Server 2003, through a compatible interface. In Windows 2000 and later versions, this protocol was often grouped under the NWLink protocol.
**Hierarchical Communication Architecture**
Network communication is typically organized into layers to simplify complexity. Each layer performs specific functions and interacts only with adjacent layers. This approach allows for modularity, easier development, and independent testing. Lower layers provide services to higher ones, while upper layers act as users of those services. This layered model helps in managing complex network tasks more efficiently.
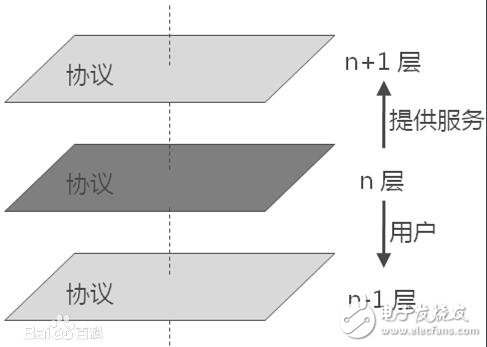
*Protocol Hierarchy Diagram*
Layering the network system enables better problem-solving and design. Each protocol operates within its own layer, ensuring that changes in one layer do not affect others, as long as the interfaces remain consistent. This makes the system more flexible and maintainable.
**Introduction to Data Communication Protocol**
A data communication protocol, also known as a data communication control protocol, is a set of standardized rules that ensure reliable and efficient communication between two parties in a data network. These rules define the format, order, and speed of data exchange, as well as mechanisms for confirming or rejecting transmissions, detecting errors, retransmitting data, and querying.
**Classification of Data Communication Protocols**
There are two main types:
- **Basic Communication Control Protocols:** Used for character-based data transmission, such as BSC (Binary Synchronous Communication).
- **Advanced Data Link Control Protocols:** Designed for bit-based transmission, like HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control) and SDLC (Synchronous Data Link Control).
**Basic Communication Control Protocol**
These protocols are typically used in simple, low-speed communication systems where the transmission speed is below 9600 bps. They operate in asynchronous or synchronous half-duplex mode, and error control is usually handled through parity checks.
**Advanced Key Control Protocol**
This type of protocol uses a standardized frame format, offering high reliability and efficiency. It is commonly used in public data networks and computer networks. Transmission speeds range from 2.4 kbps to 64 kbps, and communication occurs in synchronous full-duplex mode. Error detection is performed using cyclic redundancy checks (CRC), which improve data integrity.
Parallel groove clamps for bare neutral messenger and grounding Product information: Parallel groove clamp AL is designed to connect two parallel bare aluminum conduc- tors in low voltage cable line...
Parallel Groove Clamp,Suspension Clamp For Cable,Forging Hot-dip Galvanized Steel Parallel Groove,Parallel Groove Clamp For Aluminium
Shahe Yipeng Import and Export trading Co., LTD , https://www.yppolelinehardware.com
