According to the Boltzmann transport equation, the current density in the carrier continuity equation can be modeled using a drift-diffusion approach. In this model, the current density is expressed in terms of the Fermi levels, denoted as $ \psi_n $ and $ \psi_p $, which represent the energy levels for electrons and holes, respectively.

The mobility of electrons ($ \mu_n $) and holes ($ \mu_p $) plays a key role in determining how carriers move under the influence of an electric field. The quasi-Fermi levels are related to the carrier concentration and potential through two Boltzmann approximations, as shown below:
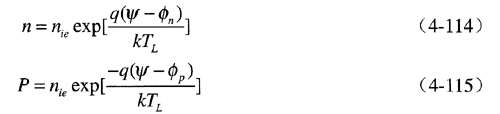
In these equations, $ n_i $ represents the effective intrinsic carrier concentration, while $ T_L $ is the lattice temperature. These expressions can then be rearranged to define the quasi-Fermi levels more explicitly:

By substituting these into the current density expression, we obtain:
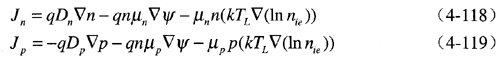
The final term accounts for the gradient of the effective intrinsic carrier concentration, incorporating the bandgap narrowing effect. The effective electric field is typically given by:
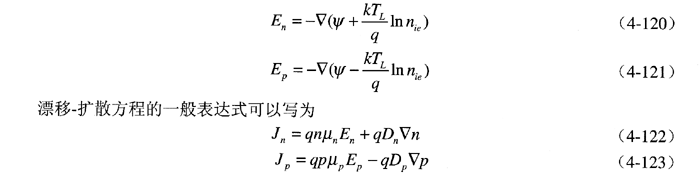
Note that the derivation of the drift-diffusion model assumes the Einstein relation. For Boltzmann statistics, this relationship is expressed as:
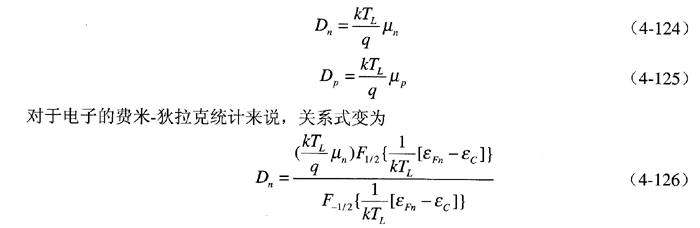
Here, $ a $ takes values of $ \pm \frac{1}{2} $, representing the a-point integrals of the Fermi-Dirac distribution, and $ \epsilon_{Fn} $ is defined as $ -qQ_n $.
This platform aims to support small and micro-enterprises by offering cost-effective advertising solutions. We recommend maintenance services and products tailored to your needs. Contact us via QQ or email for more details!
Why choose online advertising?
- 0
- like
| Try to find the information you want. Inverter sensor patch, three no weight loss camera, LCD monitor does not boot, digital camera XC9237, projector switching power supply, laptop processor, IPS USB skills, entrepreneurial, black screen, water heater cannot boot, circuit design, silent transformer, XC6102, without sound, XC6112, display regulator, no image, microwave player, successful silent GPS, tea no picture, XC6222, health, XC6372, relay filter, ML6209, switch, washing machine, digital camera description, remote control, without grating, 555 protection circuit, cancer self-closing, Linux charger, mobile phone shutdown, noise inverter, oscilloscope, robot, Windows, antenna, indicator light is not bright, fiber life, transformer, stomach market alarm, Hard disk watch, embedded system, woman maintenance process, memory, XC9236, converter, router, interview, server, kidney, RFID, LED driver, Konka, CDMA instrument, Panasonic CCD, flashing engine, multimeter, Apple liver, motor resistance, keyboard, integrated circuit, current transformer, triode, governor, power supply, LED |

XPON (Passive Optical Network) technology encompasses various types of Optical Network Units (ONUs), each designed to meet specific needs and applications. Here are the different types of XPON ONUs, based on the underlying standards and use cases:
- GPON ONU (Gigabit Passive Optical Network): Designed to operate within GPON networks, which provide high-speed data transmission, typically up to 2.5 Gbps downstream and 1.25 Gbps upstream.
- EPON ONU (Ethernet Passive Optical Network): Based on Ethernet standards, EPON ONUs provide data transmission using Ethernet packets. They typically support speeds of up to 1 Gbps.
- XGS-PON ONU (10 Gigabit Symmetric Passive Optical Network), 10G PON ONT: It supports symmetrical data rates of 10 Gbps both upstream and downstream, making it suitable for high-bandwidth applications. It is suitable for enterprise applications, high-definition video streaming, and other data-intensive services.
- Multi-Service ONU: Capable of delivering various services (internet, voice, video) through a single ONU platform. We have Data ONU , CATV ONU , VOIP ONU , WiFi 4 ONU, WiFi 5 ONU, WiFi 6 ONU. It is used in both residential and commercial environments where multiple services are provided to end-users.
The choice of an ONU type depends on various factors such as service requirements, deployment environment, and the specific standards of the optical network. Each type of ONU is designed to optimize performance, reliability, and service delivery according to its intended use case.
gepon onu,xpon ont,gpon ont,epon onu,dual band wifi onu
Shenzhen Runtop Technology Co.LTD , https://www.runtoptech.com
