Digital clock management is available in most FPGAs in the industry (all of Xilinx's FPGAs have this feature). Xilinx offers state-of-the-art FPGAs that provide digital clock management and phase loop locking. Phase loop locking provides accurate clock synthesis and reduces jitter and filtering.
4. Embedded block RAM (BRAM)Most FPGAs have embedded block RAM, which greatly expands the range and flexibility of FPGA applications. The block RAM can be configured as a common storage structure such as single port RAM, dual port RAM, content address memory (CAM), and FIFO. RAM and FIFO are relatively popular concepts and will not be redundant here. The CAM memory has a compare logic in each of its internal memory locations. The data written to the CAM is compared to each of the internal data and returns the address of all data identical to the port data, thus the address at the route. There are a wide range of applications in the switch. In addition to block RAM, the LUTs in the FPGA can be flexibly configured into structures such as RAM, ROM, and FIFO. In practical applications, the amount of internal block RAM in the chip is also an important factor in selecting a chip.
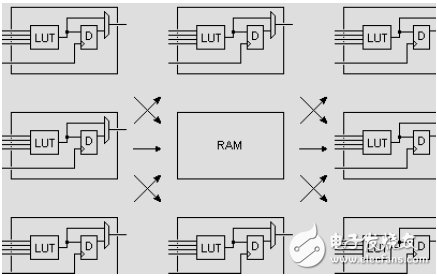
The single-chip block RAM has a capacity of 18k bits, that is, a bit width of 18 bits and a depth of 1024. The bit width and depth can be changed as needed, but two principles must be met: first, the modified capacity (bit width and depth) cannot be greater than 18k bits; secondly, the maximum bit width cannot exceed 36 bits. Of course, multiple blocks of RAM can be cascaded to form a larger RAM, which is limited only by the amount of block RAM in the chip, and is no longer bound by the above two principles.
5. Rich wiring resourcesThe routing resources connect all the cells inside the FPGA, and the length and process of the wires determine the driving capability and transmission speed of the signals on the wires. The FPGA chip has a wealth of routing resources inside, and is divided into four different categories according to the process, length, width and distribution. The first type is the global routing resource, which is used for the internal global clock of the chip and the global reset/set wiring; the second type is the long-line resource, which is used to complete the wiring of the high-speed signal between the chip Bank and the second global clock signal; Classes are short-term resources used to complete the logical interconnection and routing between basic logic cells; the fourth class is distributed routing resources for control signals such as proprietary clocks, resets, and so on.
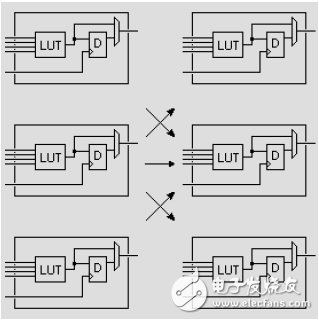
In practice, the designer does not need to directly select the routing resources, and the layout router can automatically select the routing resources to connect the various module units according to the topology and constraints of the input logical network table. In essence, there is a close and direct relationship between the use of routing resources and the results of the design.
Heaters refer to equipment used for heating. Heating equipment can be roughly divided into: gas heating equipment, electric heating equipment, boiler heating equipment, and electric wall-hung boiler heating according to different heating media and different heating principles.
Basic use of heater: It can be widely used in various civil and public buildings such as residential, office, hotel, shopping mall, hospital, school, train carriage and other mobile heating, simple mobile room and so on.
Heater product features: directly convert electrical energy or other chemical energy into heat energy, and transfer heat through radiation, convection contact, etc., so that users can move in a suitable temperature environment, and in most cases, the air humidity will be reduced.
The basic principle of heaters: use electric energy to convert into heat, and heat the environment or the human body through contact conduction, radiation, convection and other methods.
Main types of heaters:
Electric blanket-direct contact conduction; quartz tube heater-heat radiation; heater-warm air convection; air conditioner-warm air convection; electric oil heater-slow air convection; far infrared heater-simulation Far infrared radiation from the sun.
Main advantages and disadvantages of heaters:
Electric blanket-the quality is unstable, the service life is average, easy to fire, and the human body is very dry after long use;
Quartz tube heater-the quality is not very stable, the service life is average, the temperature rises slowly, it makes the air dry, and it is more harmful to the skin;
Heater-the quality is not very stable, the service life is average, the temperature rises quickly, it makes the air dry, and it is more harmful to the skin;
Air conditioner-the quality is relatively stable, some air conditioners have no heating function, have average service life, and heat up quickly, making the air dry;
Far-infrared heater-no visible light, no noise, safety, long life, can be used in open places, heating while also having physiotherapy effects (imitating the principle of solar radiation heating, heating and heating at the same time, the release wavelength is 6-15 Micron far-infrared rays can activate human cells and promote metabolism). When using, pay attention to drinking water to replenish human body moisture. Avoid long-term direct exposure to eyes and wounds. Fixed installation is required. The price is high and cannot be moved. It is suitable for people with sufficient budget.
In most cases, it is a good way to use a humidifier while heating.
Mini Household Heater,Multifunctional Household Heater,Portable Household Heater
Shenzhen YouTai Imp.&Exp.,Co.,Ltd. , https://www.szyoutai-tech.com
