First, visual work table lamp and related concepts
The desk lamp is a portable luminaire placed on the table top. According to the characteristics of visual work, the desk lamp can be divided into three types: reading and writing visual work table lamp, VDT (visual display terminal) visual work table lamp, and other table lamps.
1. Visual work table lamp is a table lamp that provides illumination for reading and writing visual work or VDT (visual display terminal) visual work.
2. Reading and writing visual work table lamps are table lamps that provide illumination for reading or writing. The working surface illuminated by the reading and writing visual work table lamp itself does not emit light. Reading and writing visual work desk lamps provide horizontal illumination.
3. In addition to being used as a reading and writing visual work table lamp, the VDT visual work table lamp is more important in that the working surface (visual display terminal) is illuminated. The VDT vision work table lamp provides both horizontal illumination and vertical illumination.
4. Other desk lamps mean that the desk lamp is not designed for visual work. For tableside cabinets, table lamps that provide vertical illumination.
Second, the visual work table lamp needs attention
1, photometric performance
a) China's national standards
GB/T 9473-2008 "Reading and writing work table lamp performance requirements" in the photometric requirements mainly have the requirements of shading and illumination and uniformity.
1) shading
Shading requirements: the height of the eyes from the reading and writing table is 400mm, and the horizontal distance from the center of the light source is 600mm. When looking at the lamp, the inner wall of the reflector and the light source should not be visible.
The shading test is shown in Figure 1.
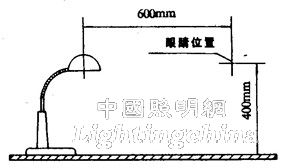
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of GB/T 9473 shading test
The height of the eye from the desk and desk is 400mm based on the height of the adult. The child's eyes may be lower than the height of the reading and writing table.
2) Illuminance and uniformity
Illuminance requirement: the vertical projection point of the geometric center of the light exit of the luminaire is centered on the front of the eye, within the projection range near the side of the eye, within a third of the radius of the center of the circle, 300A, AA illuminance Should be greater than 500lx, Class A illuminance should be greater than 250lx; a radius of 500mm from the center of the circle should be within the area of ​​the front fan-shaped cut, the AA level illumination should be greater than 300lx, and the A-level illumination should be greater than 150lx. The illuminance uniformity (maximum/minimum) in each zone must not be greater than 3. The requirements for illuminance and uniformity are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 GB/T 9473 illumination and its uniformity requirements

Illumination test: centered on the vertical projection point of the geometric center of the light exit of the luminaire, located in front of the eye, within the projection range of the luminaire, within a quarter of a radius of 500 mm from the center of the circle, at 30° intervals The illuminance measurement is performed on the radius line with a test interval of 100 mm, including the center of the circle. The illuminance test is shown in Figure 2.
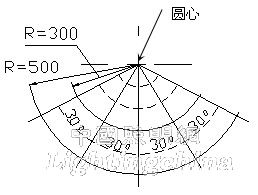
Figure 2 Distribution of GB/T 9473 illuminance test
It can be seen from Fig. 2 that GB/T 9473-2008 requires that the desk lamp illuminate a sector of 120°.
b) IESNA recommended table lamp illuminating area, illuminance and uniformity requirements
In the United States, the area requirements for the working surface of home reading and writing operations are as follows: the main working surface area is 360mm × 310mm (as shown in Figure 3); the secondary working surface area is 610mm × 910mm.
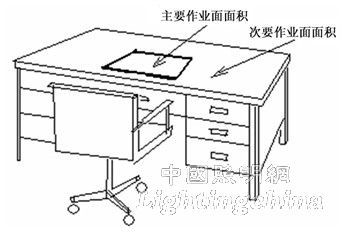
Figure 3 IESNA diagram of the illuminated area of ​​the home reading and writing work surface
Recommended values ​​for illuminance maintained at any time on the work surface: 1 main work surface - short time read or write - 200 lx, 300 lx or 500 lx; ​​2 secondary work surfaces - long learning and difficult work - 500 lx, 750 lx or 1000 Lx; 3 The ratio of the maximum illuminance to the minimum illuminance of the main working surface should not exceed 3; 4 times the main working surface - 1/2 main working surface illuminance value, but should not be less than 200 lx.
c) Japanese Industrial Standards
1) shading
Japan is revising the industry standard JIS C8112:2008 "Fluorescent Table Lamps (Learning/Reading)". The light source covered by JIS C8112 "LED Table Lamps/Fluorescent Table Lamps (Learning/Reading)" includes both fluorescent lamps and LEDs. JIS C8112 mainly has requirements for light and illuminance in terms of photometric requirements.
Light-shielding requirements: The fluorescent light of the fluorescent lamp should not be visible. The light-shielding property of the LED desk lamp should not be able to see the brightness of the LED module above 2000 cd/m2.
The shading test is shown in Figure 4.
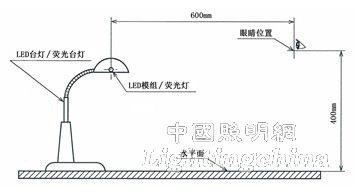
Figure 4 Shading confirmation position of JIS C8112
Since the height of the child's eyes is generally less than 400mm from the reading and writing tabletop, the light source may be visible when sitting up, so the brightness needs to be limited. The screen brightness is limited to 200cd/m2, the brightness of the LED module is limited to 2000cd/m2, and the brightness of the LED module is ten times that of the screen. The lighting effect of ten times brightness ratio is considered to be comfortable.
2) Illuminance
The illumination requirements are shown in Table 2. JIS C8112 does not have the requirement for uniformity of illumination.
Table 2 Illumination requirements of JIS C8112

The illuminance test is shown in Figure 5. As can be seen from Fig. 5, JIS C8112 requires that the table lamp illuminate the sectoral area of ​​120°, which is the same as the illuminated area of ​​GB/T 9473-2008 in China.
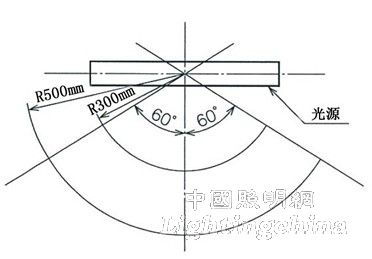
Figure 5 JIS C8112 desktop illuminance measurement range
d) "Visual Work Table Lamp Technical Requirements"
1) Illuminance and uniformity
The illuminance shall comply with the illumination requirements of Class A or AA of Article 5.8.2 of GB/T 9473, and the measurement method shall be in accordance with Article 6.8.2 of GB/T 9473.
The uniformity shall comply with the requirements of 5.8.2 of GB/T 9473, and the measurement method shall be in accordance with 6.8.2 of GB/T 9473.
2) shading
It complies with the requirements of Article 5.8.1 of GB/T 9473, and the measurement method is in accordance with Article 6.8.1 of GB/T 9473.
For a desk lamp using LED as a light source, the height of the table is 400 mm from the reading and writing table, and the horizontal distance from the center of the light source is 600 mm. When looking at the lamp, the light source of 2000 cd/m2 or more and the inner wall of the reflector or the light transmitting structure should not be seen.
3) Brightness of the lampshade
When the height of the light-emitting surface of the VDT visual work table lamp is less than 750mm in the normal working position, the person adopts the sitting position from any normal use position, and the VDT visual work table lamp with the upward beam of light has a translucent area of ​​the side of the lamp cover of not less than 10cm2. The brightness of the translucent surface should be between 510 cd/m2 and 170 cd/m2.
The VDT vision work table lamp also has a significant amount of upward beam flux, and the upper beam flux is at least 50% of the total luminous flux. Assuming that the upward luminous flux is 50% of the total luminous flux, the lower luminous flux is 97.8×2=195.6 lm according to Fig. 6, the total luminous flux of the luminaire is 97.8×4=391.2 lm, and the upward luminous flux is 195.6 lm.

Figure 6 Schematic diagram of the area and illumination of the read and write visual work surface
2, stroboscopic
a) China's national standards
GB/T 26692-2011 "Performance requirements for strobe-free electronic ballasts for tubular fluorescent lamps" In the stroboscopic aspects, there are mainly the working current waveform of the lamp and the output current frequency when the ballast is working.
1) Working current waveform of the lamp
a) Within each successive half-week, the difference in envelope waveform of the lamp current shall not exceed 4% at the same time after the supply voltage has passed through zero phase.
b) For individual high frequency crest factors, the maximum ratio of peak to rms should not exceed 1.7.
When high frequency modulation occurs at the power supply frequency, for the modulated envelope trace, the ratio of the maximum current peak output from the ballast to the lamp and the minimum current of the lamp should be no more than 1.15.
Note: The crest factor of the high frequency current is equal to the peak value of the envelope wave that has been modulated or unmodulated divided by the actual rms current.
2) Output current frequency when the ballast is working
When the ballast is working with the rated lamp, the frequency of the output current to the lamp should be in the range of 40 kHz to 50 kHz.
b) Description of the US IESNA regarding "flicker and stroboscopic effects"
All light sources that work under AC will produce flicker. The degree of flicker is observable. Depending on the frequency of the alternating current, the persistence of the light produced by the source and the viewing conditions.
The flicker acts significantly on moving objects within the viewing range. Objects may appear discrete rather than continuous under flickering illumination. This effect is known as the stroboscopic effect. The level of stroboscopic effect depends on the speed and amplitude of the flicker, as well as the rate at which the object moves and the state of observation.
The flicker index has been recognized as a reliable relative measure (value) of the output cycle variation of various sources at a given power frequency. The flicker index takes into account the waveform and amplitude of the light output. This value is calculated by dividing the area above the average line of the light output of a single curve by the area below the light output curve (see Figure 7). If the light output is a periodic peak that will vary, area 2 in Figure 7 may be close to zero.
The flicker index value is assumed to be from 0 to 1, where 0 is the steady state light output. The higher the index value, the more audible effects that can be perceived and the increased likelihood of lamp flicker.

Figure 7 Definition of flicker index and percent flashing, from the IES Tenth Edition Handbook
c) IEEE risk assessment draft "Potential health effects of LED lighting flashing"
The potential adverse effects of flashing mainly include the following five aspects:
• photosensitive epilepsy or scintillation-induced seizures;
• stroboscopic effects and associated significant slowing or stopping of the rotating machinery;
• Migraine or severe headache is often accompanied by nausea and visual disturbances;
• Increase repetitive behavior among autistic people;
• Includes strain fatigue, eye strain, blurred vision, and traditional headaches, vision, and performance degradation in vision-related work.
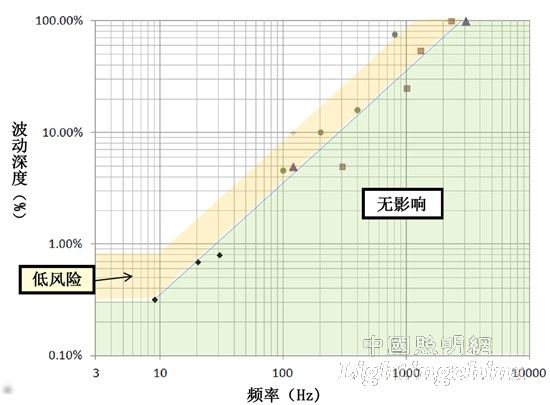
Figure 8: Relationship between flicker frequency and wave depth function for low-risk and imperceptible levels of influence
