Smaller, faster and better -this is the development trend of optical cable over the years. With the invention of dispersion compensation technology and people's attention to improving the reliability of optical fibers, "faster and better" is undoubtedly the goal advocated in the 1990s.
In recent years, the industry has focused on reducing the footprint of fiber optic networks. It can be said that with the development of smaller bend radius (RBR) fibers by fiber optic suppliers around 2005, the trend toward smaller cables and hardware has begun to appear. Shortly after the appearance of these new optical waveguide designs, people developed an international standard for regulation, namely ITU G657. Later, as the tolerances of optical fibers for macrobending and microbending gradually increased, these "knotted" fibers began to allow smaller cable designs.
Macro and micro benefits of small bending radius fiber
Macrobending is a simple phenomenon that is easy to understand. ITU G657 stipulates special optical loss specifications at special bending radii for macroscopic bending performance. However, there are some claims that the improved microbending performance comes from the main characteristics of the small bending radius to achieve smaller size and higher performance wiring. One method for actually analyzing the difference between macrobending and microbending is to imagine winding an optical fiber around your finger, measuring fiber loss (macrobending), pressing a piece of sandpaper on the fiber and measuring the corresponding Loss (microbending loss), and then compare the difference between the two.
In these two cases, the fundamental optical phenomena that cause signal loss are very different. When the optical cable is exposed to a low-temperature environment, the materials in the optical cable will tend to shrink and apply force along the length of the fiber. This force will cause the microbend of the optical fiber in the optical cable. For example, the improved microbend tolerance of optical fibers with small bend radius can undoubtedly help the optical cable withstand large temperature changes.
Global cable manufacturers are using this feature of optical fibers with small bend radius. Their "wish" is to develop an optical cable that can be used like a copper cable-strong and durable, small size, practical, anyone can easily operate, and will not damage the fiber. To achieve this goal, people have also innovated the materials used in the manufacturing process of optical cables. The bending performance of optical fibers with small bending radius has been improved, which promotes the use of new materials and new manufacturing technologies in the manufacture of optical cables, thereby making the optical cable smaller in size and lighter in weight. With these problems solved together, a new generation of optical cables with smaller size and greater flexibility can be manufactured.
A major factor of small radius optical cables is patch cords and other directly connected optical cables. In addition to the obvious benefit of being able to install more fiber optic cables in the same space, the smaller size of the fiber optic cable can also speed up the air flow because the fiber optic cable takes up less pipe space. As active electronic component suppliers try to miniaturize and merge electronic cabinets, the importance of this advantage will become more apparent. In such electronic cabinets, heat has gradually become an important issue. Generally, people will consider the airflow along the copper cable (copper cable itself will generate heat). But as equipment cabinets become smaller and hotter, all aspects of airflow become very important.
A new wave of smaller direct-connect optical cables and jumpers has begun
Smaller size, beyond your imagination
This phenomenon may not be so obvious now, but each time the diameter of a circular cable decreases by one unit, the space occupied by the cable (the area of ​​the circle) will be reduced accordingly. Therefore, a slight reduction in the diameter of the optical cable may mean that the occupied space is greatly reduced. for example:
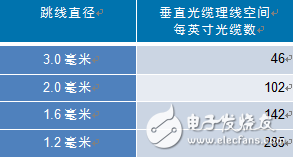
Therefore, comparing a typical 2.0-mm cable with a 1.2 mm diameter cable, it can be clearly seen that although the diameter of the cable is not reduced by half, the number of recommended cables that can be installed in the same space (1 square inch) It is as much as three times the original!
Auto Identify Technology - The LENCENT multi usb plug charger would identify the connected devices intelligently and provide optimized charging universal compatibility. It`s suitable with electronic devices and models, from iPhones, Samsungs, HTC Nexus, Mp3 Players, Bluetooth Speaker Headsets to iPads and Power Devices
High Speed Charging - Each port could offer maximum current up to 4.4A, fast-charging for any connected device efficiently, definitely you can charge 4 devices at the same time
Certified Safe - The certifications of EMC/LVD/ROHS make this travel plug a safety system with which would automatically stop charging once the devices are fully charged, or overheat, over-load, or short circuit
★Ideal for Travel - Portable Sized USB plug adapter with Interchangeable UK/USA/EU/AUS plugs and international voltage compatibility, makes it easy for multiple devices charging, anywhere you go (apply for type A / C / E / F / G / I )
Iphone Travel Charger Europe,Travel Charger Best,Travel Charger Dual Usb,Usb Travel Charger
Dongguan City Leya Electronic Technology Co. Ltd , https://www.dgleya.com
