Wi-Fi is a brand of wireless network communication technology and is held by the Wi-Fi Alliance. The purpose is to improve the interoperability between wireless network products based on the IEEE 802.11 standard. At present, most people will confuse Wi-Fi and IEEE 802.11. It even equates Wi-Fi to wireless Internet. Wi-Fi is blowing the horn of battle to completely replace other wireless communication protocols, and Intel is undoubtedly the rear of this battle. GainSpan, a startup spin-off from Intel in September 2006, claimed that they already have a technical solution to overcome Zigbee in the field of wireless sensor networks (WSN). GainSpan President and CEO Vijay Parmar said in an interview in Shanghai not long ago that adopting the company ’s WSN solution will not only enjoy the benefits of mature Wi-Fi technology, but also ensure that the The battery can maintain a battery life of up to 5 to 10 years.
In addition to visiting existing clients, Parmar's trip to China also included the first meeting of small journalists in mainland China, which was intended to build momentum for its already opened Chinese business. According to reports, this SoC chip manufactured in TSMC's 0.18 micron process uses an ARM7 core, can support IEEE 802.11b / g, and provides 802.11i, AES encoding, EAP-FAST three ways to ensure data and information security. In addition, according to the signal strength and time of arrival (TDOA) size, it can also provide accurate positioning function. The chip size is 10mmx10mm. Currently, the company is actively building partnerships with universities and government agencies, and has signed a distribution agreement with Metatech. Parmar said he plans to use six months to establish a representative office in mainland China, with Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen as candidate cities.
Intel is not only the breeder of GainSpan, but also has given this emerging company huge financial support in two rounds of financing. In September 2006, due to the fact that the main business of the parent company was not very relevant, when a WSN technology development team belonging to Intel ’s new business planning group was decided to split from Intel, a startup called GainSpan was established Focus on applying Wi-Fi technology to WSN networks in the industrial field. Intel Capital, New Venture Partners LLC, OVP Venture Partners, Sigma Partners and other four investment companies provided a total of US $ 1.5 million in startup capital.
In November 2007, Intel once again joined other three companies and brought in another venture capital company Opus Capital, based in Menlo Park, California, to make a second round of investment in GainSpan. The amount of investment in this round jumped to 20 million US dollars.
Using Wi-Fi for WSN networks is indeed a good idea. Because it can enjoy the mature technology brought by the large-scale deployment of Wi-Fi networks, various endless Wi-Fi devices, existing network facilities, architectural support, rich network knowledge, and fast Installed and reduced the various troubles caused by the learning cycle and interoperability with other protocols, speeding up the development cycle.
However, using Wi-Fi for WSN is not an easy task. Because in this application, the first problem that needs to be solved is the power consumption problem-fortunately, GainSpan has already made it easy. Although no more technical details were disclosed, Parmar said that effective activation / standby state transition and system power management are the key to achieving this target. The case can achieve a 5 to 10 year life of an AA battery. We are the only company that can do this.
Before leading the team to establish GainSpan in 2006, Parmar worked for Intel for about 4 years. Earlier work experience was as Vice President of Marketing at VxTel (a VoIP solution provider), which was acquired by Intel in 2001. Earlier, he worked for AMD and served as the general manager of AMD ’s regional markets for microprocessors in the Asia-Pacific region. This makes him quite familiar with the Chinese market.
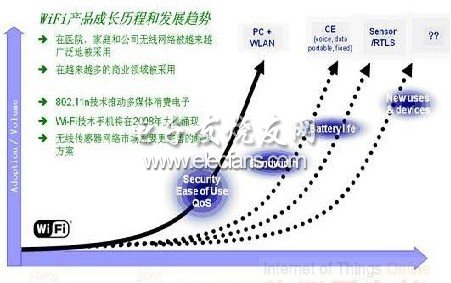
To talk about WSN, it is necessary to mention Zigbee, in fact, this technology has already established a foothold in the field of WSN. How does the coming Wi-Fi compete with it? Parmar believes that Zigbee is far behind Wi-Fi in terms of security, technological maturity, connection with existing networks, node management, QoS characteristics, and device interoperability. . "And these are exactly what customers need." He said.
The advantages of Wi-Fi in WSN networks are not limited to this. Parmar pointed out that the rising boom in Wi-Fi network construction has made Wi-Fi the mainstream direction of wireless networks. Using existing Wi-Fi network resources to deploy and implement WSN will save a lot of hardware costs. In addition, there is no need to consider interoperability with other devices such as Zigbee. It will also help project implementers shorten the development cycle, which also means lower project implementation costs. Of course, mature Wi-Fi also has the advantages of existing architecture support and fast installation. "In short, using Wi-Fi for sensor networks will help maximize the return on investment (ROI) and total cost of ownership (TCO)." Parmar said, "Although Zigbee has the advantages of small size and low unit price, but Once the overall cost is considered, they are still much more expensive. "
Complete solution
To help customers shorten the development cycle, GainSpan also provides a complete set of software and hardware tools including SDK, evaluation platform, and development platform. Its software stack includes various I / O drivers and WLAN firmware, RTOS, network stack, system services, WLAN and I / O service modules, various application programming interfaces, and application software. Parmar claims that the GS1010 SDK can help engineers save 10 to 12 months of development time. The hardware development platform can support various sensors such as temperature, humidity, light sensitivity, pressure, acceleration, etc., and reserves the sensor interface and debugging and program burning interface of the customer's choice.
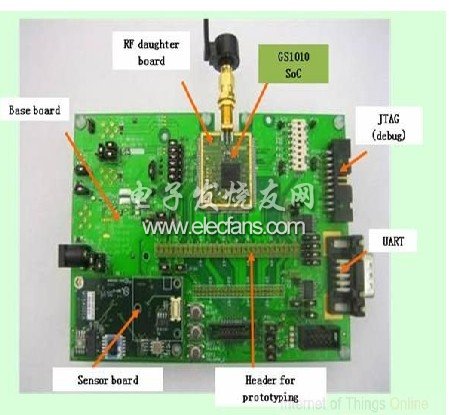

In addition to the chip itself, the client management software GMS control system also plays a big role in taking advantage of Wi-Fi. The real-time interface helps the system to control and use a single-hop network to manage the nodes to maximize the battery life of the client device. Supporting standard network protocols such as SNMP and UDP makes Wi-Fi WSN compatible with existing network systems such as industrial control, building automation, and enterprise network management systems. The software can also effectively configure, control and monitor sensor nodes, realize intelligent centralized control and management, and support firmware upgrades. In addition, the intelligent data processing capability can also centrally manage, preprocess and summarize the data collected by the sensors.

GainSpan started mass production of GS1010 in Q4 last year. Parmar said, "Aginova and RF Digital have already launched products using our chips in May this year."
The accessories for FTTx includes the optical adapters SC/LC/FC/ST, the Drop Cable Protection Box, the splice sleeves and so on
Adapter, blue color sc/upc lc/upc fc/upc single mode
green color sc/apc lc/apc single mode
gray color sc/pc lc/pc fc/pc st/pc
aqua color sc/pc lc/pc fc/pc st/pc OM3
purple sc/pc lc/pc fc/pc st/pc OM4
Drop Cable Protection Box, one fiber and two fibers
Splice sleeves: one steel 45/60mm for general cable and two steels 45/60mm for drop cable
Fiber Optic Connector,Fiber Distribution Panel,Fiber Cable Connectors,Fiber Adapter
Chengdu Xinruixin Optical Communication Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.xrxoptic.com
