In the context of the Internet of Everything, the application of the Internet of Things has become increasingly sophisticated, and edge computing has gradually gained attention and is now frequently discussed. The emergence of edge computing has significantly improved network transmission performance, and a substantial amount of investment has been directed toward its widespread adoption. Moreover, major industry players are actively competing to establish their presence in this field, making it clear that the future of edge computing is already taking shape.
With the rising popularity of cloud computing, edge computing has also seen a surge in interest. Some have referenced the saying from *Romance of the Three Kingdoms*—“Great things in the world must be divided, and long-term strategies must be combinedâ€â€”to describe the relationship between cloud and edge computing. However, edge computing is not a new concept. IBM introduced the idea through its IoT ecosystem map in 2012, bringing it into the spotlight for the first time.
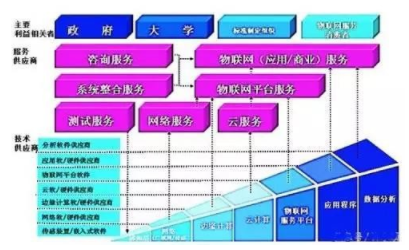
**IBM IoT Eco Map**
**First, is edge computing a hype or a trend?**
In today’s fast-paced technological landscape, the rise of the Internet of Everything means that an increasing number of IoT devices are being connected to the network. According to Gartner, by 2020, there will be over 26 billion connected devices. As these devices generate massive amounts of data, they bring both commercial value and significant challenges in terms of data processing.
The sheer volume of data produced at the network edge has placed a heavy burden on cloud computing centers. Traditional cloud models can no longer keep up with the demands of real-time data processing, bandwidth limitations, and data privacy concerns. According to IDC, global data will exceed 40ZB by 2020. Due to these constraints, edge computing has emerged as a critical trend in the evolution of the Internet of Things.
**Second, edge computing is finding more practical applications.**
In the era of big data 2.0, where data types are more complex and diverse, edge computing enhances data transmission efficiency, ensures real-time processing, and offers users a smarter and faster experience. With increased investment, edge computing is becoming more widely adopted across various industries.
1. **Smart Homes**
Many smart home devices currently rely on cloud-based systems via Wi-Fi modules. However, this approach often falls short in enabling seamless communication between devices. Edge computing supports different interaction scenarios in smart homes, typically implemented through gateways or central control systems.
2. **Smart Traffic**
As traffic data grows, user demand for real-time information increases. Transmitting all data to the cloud leads to issues like bandwidth waste and delays. By analyzing and processing data at the edge, users can get real-time updates and make informed decisions. Edge computing plays a key role in intelligent traffic control, vehicle networks, and even autonomous driving.
3. **Smart Cities**
For location-based services such as transportation and facility management, edge computing outperforms cloud computing in terms of location recognition. It allows real-time processing of geolocation data without the need to send it to a centralized cloud.
**Third, major companies are investing heavily in edge computing.**
1. **China Unicom**
At the ITU-T SG20 WP1 Plenary Session, China Unicom successfully proposed an international standard project on IoT requirements for edge computing—the first such initiative in the IoT domain. This marks a significant step in global edge computing standardization.
China Unicom is also exploring edge computing through Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC), focusing on building a robust business platform. Currently, it has launched MEC pilots in six cities and established one of the largest edge cloud virtualization test beds, involving over 50 partners.
2. **ARM**
In 2017, ARM introduced PSA for IoT security and Mbed Edge for enhanced edge management. Mbed Edge enables users to expand device management capabilities through IoT gateways, supporting features like device onboarding, control, and diagnostics.
Key advantages include protocol translation, gateway channel management, and edge computing capabilities that allow independent operation even when disconnected from the cloud.
3. **ZTE Corporation**
ZTE has developed comprehensive edge computing solutions, covering technologies like virtualization, containerization, high-precision positioning, and CDN sinking. These solutions support six major use cases, including service localization and car networking.
ZTE emphasizes that edge computing can create new value chains and ecosystems, enhancing collaboration across the industry.
4. **Marvell and Pixeom**
At CES 2018, Marvell and Pixeom demonstrated an efficient edge computing system using Marvell’s MACCHIATObin board and Pixeom’s software. This solution extends cloud capabilities to the edge, enabling video analytics and reducing latency.
**Fourth, looking ahead.**
Edge computing integrates various IoT technologies such as peer-to-peer networks, fog computing, blockchain, and CDNs, with applications spanning multiple sectors. While cloud computing will still play a vital role, the rapid growth of IoT and the rise of edge computing are set to transform the industry soon.
From April 25 to 27, 2018, the 1018th International Internet of Things Expo was held in Suzhou, showcasing cutting-edge solutions in edge computing, smart manufacturing, AI, and more. This event provided a valuable platform for industry professionals to exchange ideas and explore new opportunities.
F Female To Rca Male,F To Rca Coaxial Adapter,F Female To Rca Male Adapte,Rca Male Rf Coaxial Adapter
Changzhou Kingsun New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.aioconn.com
